Most tech discussions today arrive at the same conclusion: the future of big data is edge computing.
While discussions around edge computing are not necessarily new, the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) has clarified how critical establishing the right presence at the edge can be.

Market demands are increasing at an incredible speed.
Decreasing cost of computer components, mobile computing and IoT devices are the main drivers toward edge computing.
All industries worldwide will soon have to leverage on edge computing and the data gathered at a higher rate in order to stay competitive and relevant. Reduced cost in service by monitoring hardware condition and sending alerts before problems appear, avoiding breakdowns, is just one of many ways to monetize from edge computing.
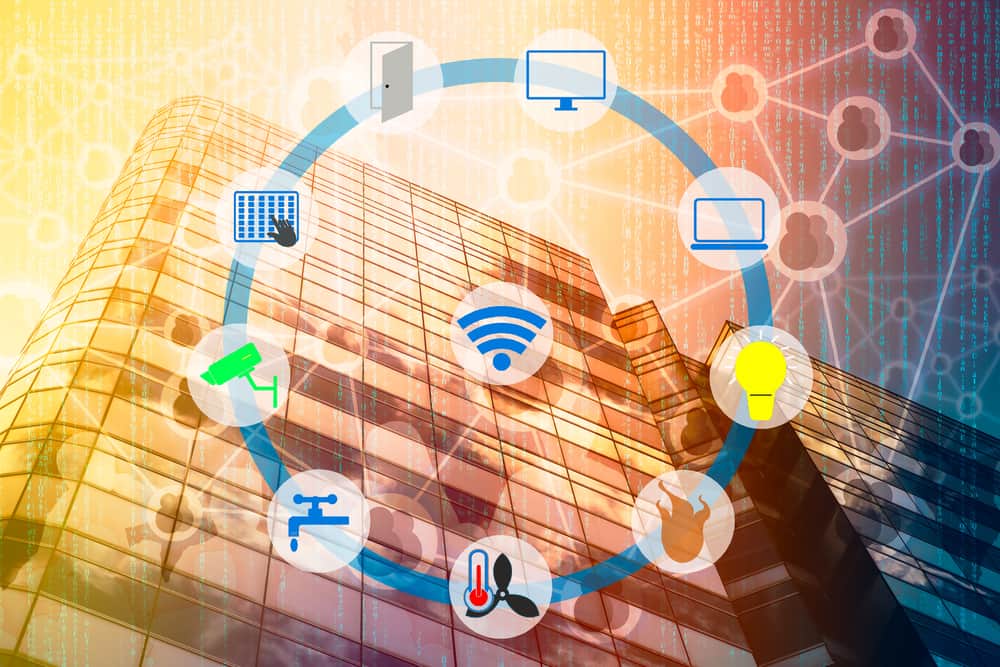
Edge computing is broadly used in verticals like aerospace and defense, oil and gas wells, automotive condition monitoring, smart buildings and in any case that will need high speed in memory OLTP (On-line Transaction Processing) data to be stored on the edge.
How to tackle the demands of today’s edge computing environment?
- First of all, you need to have an edge computing strategy. Most companies already have edge computing devices, but they do not leverage all the data they potentially can use.
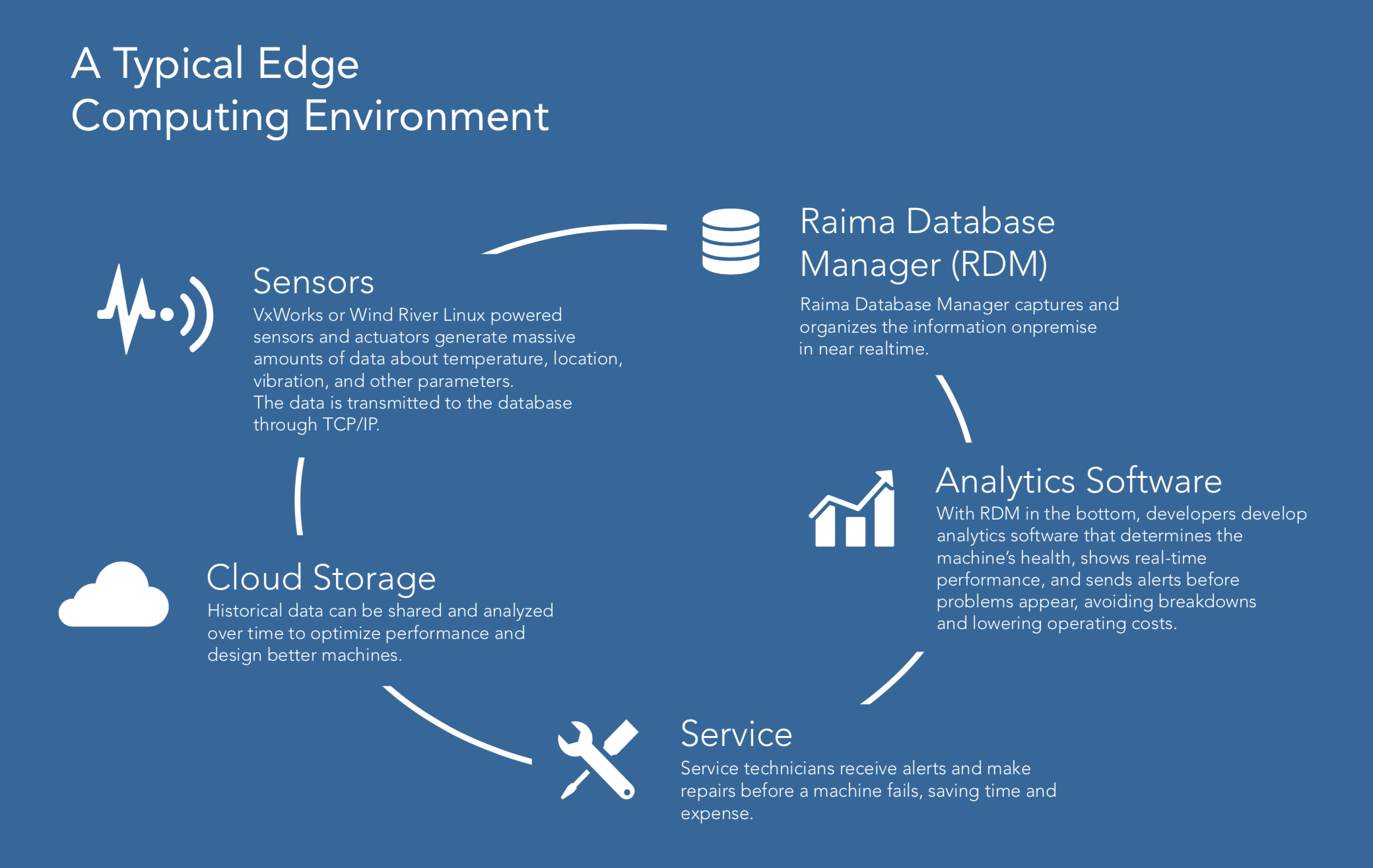
- It starts with the sensors and actuators that need an operating system like Wind River® VxWorks® real-time operating system or Wind River Linux.
- Then you need a database engine that enables the operating system to be a smarter content management system. A database system like RaimaDB captures and organizes the information on-premise in near real time.
- An analytics software processes the data that determines the health, shows real time performance and sends alerts before problems appear, avoiding breakdowns and lowering operating costs.
- Historical data can then be pushed to the cloud and analyzed over time to make sure the right decisions will be made for the future.
Raima and Wind River enable time-sensitive data in an edge architecture to be processed on-premise and sending data that is less time sensitive to the cloud for historical analysis and storage.
With the recent release of RDM 14.1, RaimaDB is now perfectly designed for VxWorks and Wind River Linux to provide new value in database management, accommodating the huge demand for reliable data storage collected on the edge/on-premise and pushed up to the cloud.
Rely on RaimaDB and Wind River to help navigate cloud, IoT and IIoT application demands.
Originally published on the Wind River Blog.