IoT devices are gathering massive amounts of data all over the world, every second. These edge applications require a database that is capable of collecting these large volumes of information, storing that data reliably, and providing intuitive methods for managing that information quickly.
And being able to move that data in near real-time up into large cloud-based systems so that the most up-to-date and relevant data ultimately ends up available to those that must have immediate access to that information so that proper decisions and actions can be taken.
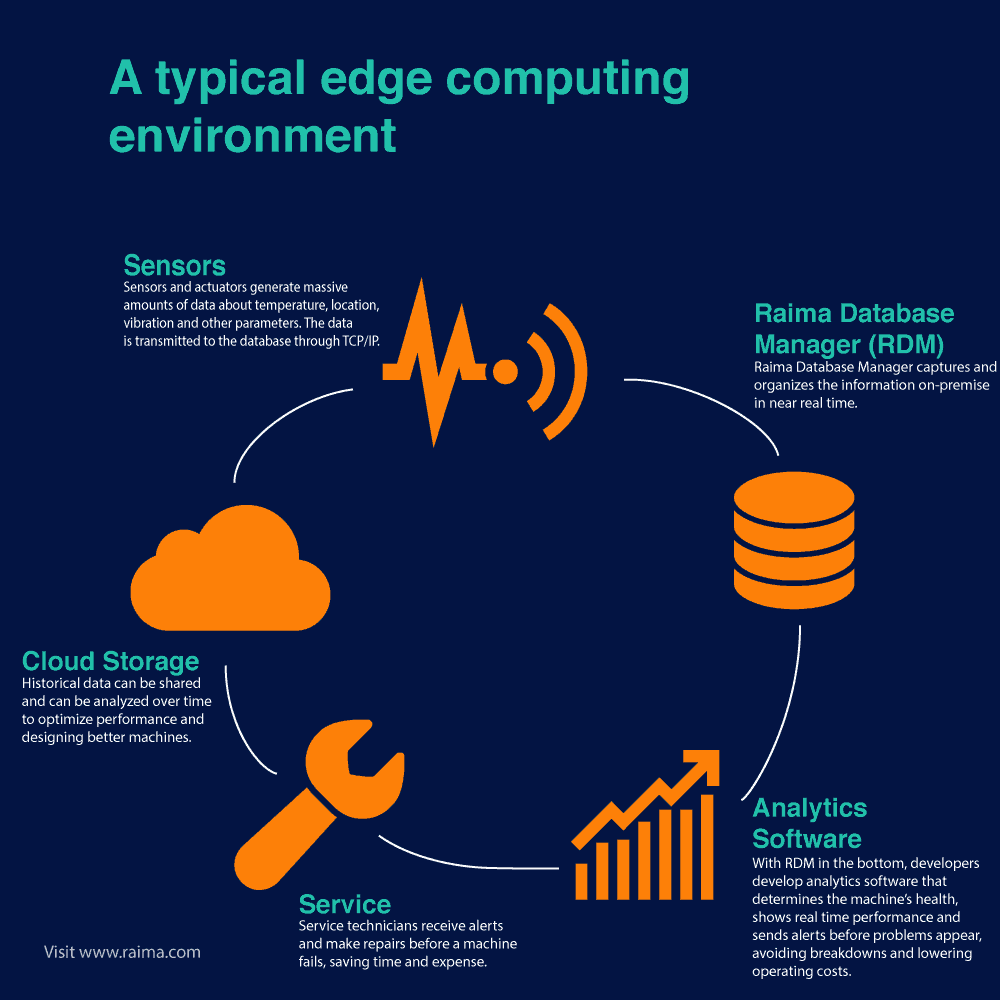
The content of the edge computing infographic:
1.Sensors
Sensors and actuators generate massive amounts of data about temperature, location, vibration and other parameters. The data is transmitted to the database through TCP/IP.
2.Database (RDM)
Raima Database Manager captures and organizes the information on-premise in near real time.
3.Analytics Software
With RDM in the bottom, developers develop analytics software that determines the machine’s health, shows real-time performance and sends alerts before problems appear, avoiding breakdowns and lowering operating costs.
4.Service
Service technicians receive alerts and make repairs before a machine fails, saving time and expense.
5.Cloud Storage
Historical data can be shared and can be analyzed over time to optimize performance and designing better machines.
Rely on RDM to help navigate cloud, IoT and IIoT application demands.